Discussion Questions
1. Select an interval/ratio variable from any of the SPSS modules and discuss the properties associated with its level of measurement. Why do interval/ratio variables retain the properties of nominal and ordinal variables, yet the opposite is not true? What are these properties? Next, as a class or small group, recode this variable. See if you can transform it into an ordinal or nominal level variable. For example, a variable of interest might be annual income measured in U.S. dollars. By simply recoding this variable, we can view income as an ordinal variable measured in dollar intervals (e.g., $20,000–$29,999, $30,000–$39,000) or as a nominal variable with two discrete categories (e.g., $25,000 or ~$25,000).[1]
2. Are there any research questions or specific hypotheses where it would be advisable to study the entire population, as opposed to just a sample? If so, what characterizes these situations? Which types of research questions and hypotheses lend themselves to a study of the entire population? Which types do not and why?
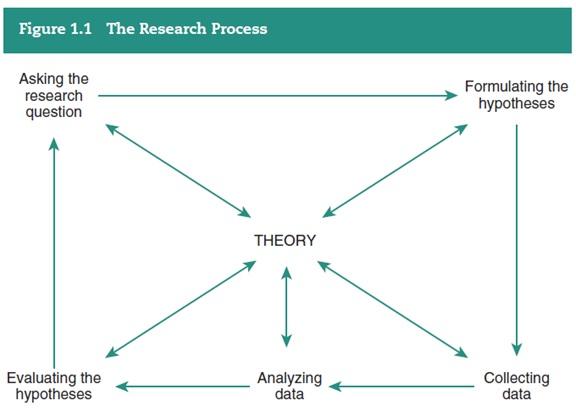
3. Figure 1.1 in the textbook characterizes the research process as a largely iterative process involving five stages with theory entering in at each. Discuss how theory informs and is informed by:
(a) asking the research question,
(b) formulating hypotheses,
(c) collecting data,
(d) analyzing data, and
(e) evaluating hypotheses.
Does theory affect any of these stages disproportionately? Why or why not?
4. What would result if the steps in the scientific research method were performed out of order? For example, what would happen if we include every variable of a data set into an analysis, find significant relationships, and then find literature and theories that support what we find?
5. Imagine that you worked for a large corporation and they asked you to “fudge” data in a manner that would financially benefit the company. How would you respond to this request?
6. Discuss a situation in which a large national data set of private information fell into the hands of an unintended person(s). What was the result of this violation?
7. Discuss how statistical presentation can be used to learn about the characteristics and experiences of minority groups in the States. Could you give an example to illustrate your answers?
[1] The logical operator, ~, refers to the negation of the statement. So, in this example, ~$25,000 means “not $25,000.”
